PartⅠWriting (30 minutes)
Directions:For this part, you are allowed 30 minutes to write a short essay on the importance of speaking ability and how to
develop it. You should write at least 120 words but no more
than 180 words.
Part ⅡListening Comprehension
Part ⅢReading Comprehension (40 minutes) Section A
Directions: I n this section, there is a passage with ten blanks. You are required to select one word for each blank from a list of
choices given in a word bank following the passage. Read the
passage through carefully before making your choices. Each
choice in the bank is identified by a letter. Please mark the
corresponding letter for each item on Answer Sheet 2 with a
single line through the centre. You may not use any of the
words in the bank more than once.
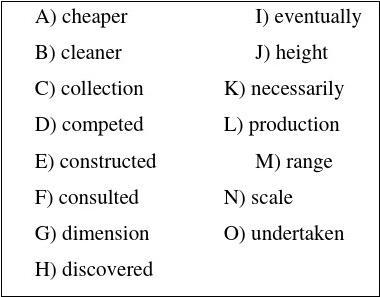
An office tower on Miller Street in Manchester is completely covered in solar panels. They are used to create some of the energy used by the insurance company inside. When the tower was first 26 in 1962, it was covered with thin square stones. These small square stones became a problem for the building and continued to fall off the face for 40 years until a major renovation was 27 . During this renovation the
1
building’s owners, CIS, 28 the solar panel company, Solarcentury. They agreed to cover the entire building in solar panels. In 2004, the completed CIS tower became Europe’s largest 29 of vertical solar panels. A vertical solar project on such a large 30 has never been repeated since.
Covering a skyscraper with solar panels had never been done before, and the CIS tower was chosen as one of the “10 best green energy projects”. For a long time after this renovation project, it was the tallest building in the United Kingdom, but it was 31 overtaken by the Millbank Tower.
Green buildings like this aren’t 32 cost-efficient for the investor, but it does produce much less pollution than that caused by energy 33 through fossil fuels. As solar panels get 34 , the world is likely to see more skyscrapers covered in solar panels, collecting energy much like trees do. Imagine a world where building the tallest skyscraper wasn’t a race of 35 , but rather one to collect the most solar energy.
2
Section B
Directions: In this section, you are going to read a passage with ten statements attached to it. Each statement contains
information given in one of the paragraphs. Identify the
paragraph from which the information is derived. You may
choose a paragraph more than once. Each paragraph is
marked with a letter. Answer the questions by marking the
corresponding letter on Answer Sheet 2.
Some College Students Are Angry That They Have to Pay to Do
Their Homework
A) Digital learning systems now charge students for access codes needed
to complete coursework, take quizzes, and turn in homework. As universities go digital, students are complaining of a new hit to their finances that’s replacing—and sometimes joining—expensive textbooks: pricey online access codes that are required to complete coursework and submit assignments.
B) The codes—which typically range in price from $80 to $155 per
course—give students online access to systems developed by education companies like McGraw Hill and Pearson. These companies, which long reaped big profits as textbook publishers, have boasted that their new online offerings, when pushed to students through universities they partner with, represent the future of the industry.
C) But critics say the digital access codes represent the same
profit-seeking ethos(观念) of the textbook business, and are even
3
harder for students to opt out of. While they could once buy second-hand textbooks, or share copies with friends, the digital systems are essentially impossible to avoid.
D) “When we talk about the access code we see it as the new face of the
textbook monopoly(垄断), a new way to lock students around this system,” said Ethan Senack, the higher education advocate for the U.S.
Public Interest Research Group, to BuzzFeed News. “Rat her than $250 (for a print textbook) you’re paying $120,” said Senack. “But because it’s all digital it eliminates the used book market and eliminates any sharing and because homework and tests are through an access code, it eliminates any ability to opt o ut.”
E) Sarina Harper, a 19-year-old student at Virginia Tech, was faced with a
tough dilemma when she first started college in 2015—pay rent or pay to turn in her chemistry homework. She told BuzzFeed News that her freshman chemistry class required her to use Connect, a system provided by McGraw Hill where students can submit homework, take exams and track their grades. But the code to access the program cost $120—a big sum for Harper, who had already put down $450 for textbooks, and had rent day approaching.
F) She decided to wait for her next work-study paycheck, which was
typically $150-$200, to pay for the code. She knew that her chemistry grade may take a dive as a result. “It’s a balancing act,” she said. “Can
I really afford these access codes now?” She didn’t hand in her first
two assignments for chemistry, which started her out in the class with
a failing grade.
4
G) The access codes may be another financial headache for students, but
for textbook businesses, they’re the future. McGraw Hill, which controls 21% of the higher education market, reported in March that its digital content sales exceeded print sales for the first time in 2015.
The company said that 45% of its $140 million revenue in 2015 “was derived from digital products.”
H) A Pearson spokesperson told BuzzFeed News that “digital materials
are less expensive and a good investment” that offer new features, like audio texts, personalized knowledge checks and expert videos. Its digital course materials save students up to 60% compared to traditional printed textbooks, the company added. McGraw Hill didn’t respond to a request for comment, but its CEO David Levin told the Financial Times in August that “in higher education, the era of the printed textbook is now over.”
I) The textbook industry insists the online systems represent a better deal
for students. “These digital products aren’t just mechanisms for students to submit homework, they offer all kinds of features,” David Anderson, the executive director of higher education with the Association of American Publishers, told BuzzFeed News. “It helps students understand in a way that you can’t do with print homework assignments.”
J) David Hunt, an associate professor in sociology at Augusta University, which has rolled out digital textbooks across its math and psychology departments, told BuzzFeed News that he understands the utility of using systems that require access codes. But he doesn’t require his
5
students to buy access to a learning program that controls the class assignments. “I try to make things as inexpensive as possible,” said Hunt, who uses free digital textbooks for his classes but designs his own curriculum. “The online systems may make my life a lot easier but I feel like I’m giving up control. The discussions are the thi ngs where my expertise can benefit the students most.”
K) A 20-year-old junior at Georgia Southern University told BuzzFeed News that she normally spends $500-$600 on access codes for class.
In one case, the professor didn’t require students to buy a textbook, just an access code to turn in homework. This year she said she spent $900 on access codes to books and programs. “That’s two months of rent,” she said. “You can’t sell any of it back. With a traditional textbook you can sell it for $30-$50 and that helps to pay for your new semester’s books. With an access code, you’re out of that money.”
L) Benjamin Wolverton, a 19-year-old student at the University of South Carolina, told BuzzFeed News that “it’s ridiculous that after paying tens of thousands in tuition we have to pay for all these access codes to do our homework.” Many of the access codes he’s purchased have been required simply to complete homework or quizzes. “Often it’s only 10% of your grade in class,” he said. “You’re paying so much money for something that hardly affects your grade—but if you didn’t have it, it would affect your grade enough. It would be bad to start out at a B or C.” Wolverton said he spent $500 on access codes for digital books and programs this semester.
M) Harper, a poultry (家禽) science major, is taking chemistry again this
6
year and had to buy a new access code to hand in her homework. She rented her economics and statistics textbooks for about $20 each. But her access codes for homework, which can’t be rented or boug ht second-hand, were her most expensive purchases: $120 and $85.
N) She still remembers the sting of her first experience skipping an assignment due to the high prices. “We don’t really have a missed assignment policy,” she said. “If you miss it, you just miss it. I just got zeros on a couple of first assignments. I managed to pull everything back up. But as a scared freshman looking at their grades, it’s not fun.”
36. A student’s yearly expenses on access codes may amount to their rent
for two months.
37. The online access codes may be seen as a way to tie the students to
the digital system.
38. If a student takes a course again, they may have to buy a new access
code to submit their assignments.
39. McGraw Hill accounts for over one-fifth of the market share of
college textbooks.
40. Many traditional textbook publishers are now offering online digital
products, which they believe will be the future of the publishing business.
41. One student complained that they now had to pay for access codes in
7
addition to the high tuition.
42. Digital materials can cost students less than half the price of
traditional printed books according to a publisher.
43. One student decided not to buy her access code until she received the
pay for her part-time job.
44. Online systems may deprive teachers of opportunities to make the
best use of their expertise for their students.
45. Digital access codes are criticized because they are profit-driven just
like the textbook business.
Section C
Directions: There are 2 passages in this section. Each passage is followed by some questions or unfinished statements. For each
of them there are four choices marked A), B), C) and D). You
should decide on the best choice and mark the corresponding
letter on Answer Sheet 2 with a single line through the centre. Passage One
Questions 46 to 50 are based on the following passage.
For thousands of years, people have known that the best way to understand a concept is to explain it to someone else. “While we teach, we learn,” said Roman philosopher Seneca. Now scientists are bringing
8
this ancient wisdom up-to-date. They’re documenting why teaching is such a fruitful way to learn, and designing innovative ways for young people to engage in instruction.
Researchers have found that students who sign up to tutor others work harder to understand the material, recall it more accurately and apply it more effectively. Student teachers score higher on tests than pupils who’re learning only for their own sake. But how can children, still learning themselves, teach others? One answer: They can tutor younger kids, Some studies have found that first-born children are more intelligent than their later-born siblings (兄弟姐妹). This suggests their higher IQs result from the time they spend teaching their siblings. Now educators are experimenting with ways to apply this model to academic subjects. They engage college undergraduates to teach computer science to high school students, who in turn instruct middle school students on the topic.
But the most cutting-edge tool under development is the “teachable agent”—a computerized character who learns, tries, makes mistakes and asks questions just like a real-world pupil. Computer scientists have created an animated (动画的) figure called Betty’s Brain, who has been “taught” about environmental science by hundreds of middle school students. Student teachers are motivated to help Betty master certain materials. While preparing to teach, they organize their knowledge and improve their own understanding. And as they explain the information to it, they identify problems in their own thinking.
Feedback from the teachable agents further enhances the tutors’ learning. The agents’ questions compel student tutors to think and explain the materials in different ways, and watching the agent solve problems allows them to see their knowledge put into action.
Above all, it’s the emotions one experiences in teaching that
9
facilitate learning. Student tutors feel upset when their teachable agents fail, but happy when these virtual pupils succeed as they derive pride and satisfaction from someone else’s accomplishment.
46. What are researchers rediscovering through their studies?
A) Seneca’s thinking is still applicable today.
B) Better learners will become better teachers.
C) Human intelligence tends to grow with age.
D) Philosophical thinking improves instruction.
47. What do we learn about Betty’s Brain?
A) It is a character in a popular animation.
B) It is a teaching tool under development.
C) It is a cutting-edge app in digital games.
D) It is a tutor for computer science students.
48. How does teaching others benefit student tutors?
A) It makes them aware of what they are strong at.
B) It motivates them to try novel ways of teaching.
C) It helps them learn their academic subjects better.
D) It enables them to better understand their teachers.
49. What do students do to teach their teachable agents?
A) They motivate them to think independently.
B) They ask them to design their own questions.
C) They encourage them to give prompt feedback.
D) They use various ways to explain the materials.
50. What is the key factor that eases student tutors’ learning?
10
A) Their sense of responsibility. C) The learning strategy acquired.
B) Their emotional involvement. D) The teaching experience gained.
Passage Two
Questions 51 to 55 are based on the following passage.
A new batch of young women—members of the so-called Millennial (千禧的) generation—has been entering the workforce for the past decade. At the starting line of their careers, they are better educated than their mothers and grandmothers had been—or than their young male counterparts are now. But when they look ahead, they see roadblocks to their success. They believe that women are paid less than men for doing the same job. They think it’s easier for men to get top executive jobs than it is for them. And they assume that if and when they have children, it will be even harder for them to advance in their careers.
While the public sees greater workplace equality between men and women now than it did 20-30 years ago, most believe more change is needed. Among Millennial women, 75% say this country needs to continue making changes to achieve gender equality in the workplace, compared with 57% of Millennial men. Even so, relatively few young women (15%) say they have been discriminated against at work because of their gender.
As Millennial women come of age they share many of the same views and values about work as their male counterparts. They want jobs
11
本文来自投稿,不代表微盟圈立场,如若转载,请注明出处:https://www.vm7.com/a/wendang/112446.html




